TECHNOLOGY, CASE STUDY, PRESS
Laser Scanning as a Method for Checking the Flatness of Construction Site Floors
Technical article in the Austrian magazine “Vermessung & Geoinformation 3/2025”
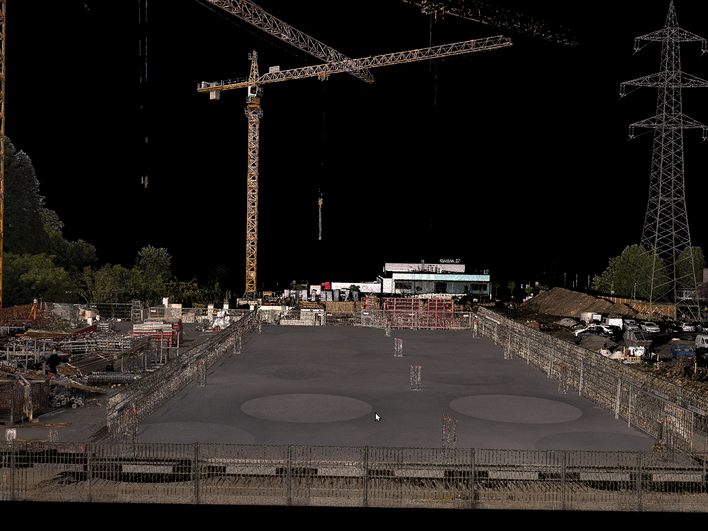
Flatness measurement of construction site floors has been regulated by standards for decades and is typically carried out using traditional methods such as straightedges, measuring wedges, or point-by-point leveling. The use of terrestrial laser scanners in this application area is still rare and is not explicitly addressed in standards such as DIN 18202. This paper investigates whether, and to what extent, modern terrestrial laser scanning – exemplified by the RIEGL VZ-600i – can serve as an alternative method for standards-compliant flatness measurement of industrial floors.
After introducing the fundamentals of flatness testing, in particular the definition of flatness deviation over a defined measurement spacing and the grid leveling method, the basic functionality and measurement characteristics of a 3D laser scanner are described. It is shown that the high point density and full-area data acquisition provided by laser scanning can form a suitable basis for flatness evaluation.
The practical application is demonstrated using a new construction project with a floor area of approximately 450 m². The area was fully captured in a short time during ongoing construction activities through multiple laser scans. The registration and adjustment of the scan positions, as well as further data processing, were performed using the RiSCAN PRO software. Based on the adjusted point cloud, elevation points were determined on a regular 50-cm grid. By averaging neighboring measurement points, measurement noise was reduced, resulting in high accuracy of the elevation determination.
The flatness deviation was subsequently calculated according to the principle of grid leveling and compared with the permissible limits specified in DIN 18202. The results show that terrestrial laser scanning enables standards-compliant, full-coverage flatness measurement. Critical areas exceeding the limits can be clearly identified and selectively inspected on site.
Overall, the study demonstrates that terrestrial laser scanning represents an efficient and practical complement to traditional measurement methods, offering significant advantages in terms of completeness, traceability, and time efficiency, particularly for large-scale industrial floors.
The article was published in GERMAN LANGUAGE in issue 3/2025 of the Austrian magazine vgi “Vermessung & Geoniformation” (Surveying & Geoinformation).


